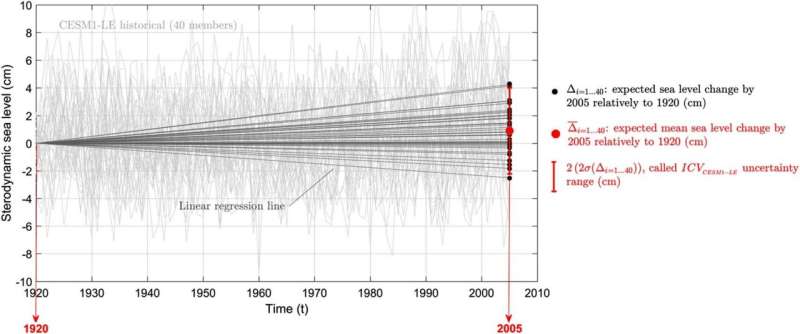
The study showed that internal climate variability could increase sea level rise in some locations by 20–30% more than what would result from climate change alone, exponentially increasing extreme flooding events. In Manila, for example, coastal flooding events are predicted to occur 18 times more often by 2100 than in 2006, based solely on climate change. But, in a worst-case scenario, they could occur 96 times more often based on a combination of climate change and internal climate variability.