Caption for figure above: Grid-cell specific rankings of 22-yr negative soil moisture anomalies (drought rank) in 2000–2021 compared to the driest 22-yr period in each previous drought event back to year 800. ACC is an initialism for Anthropogenic Climate Change.
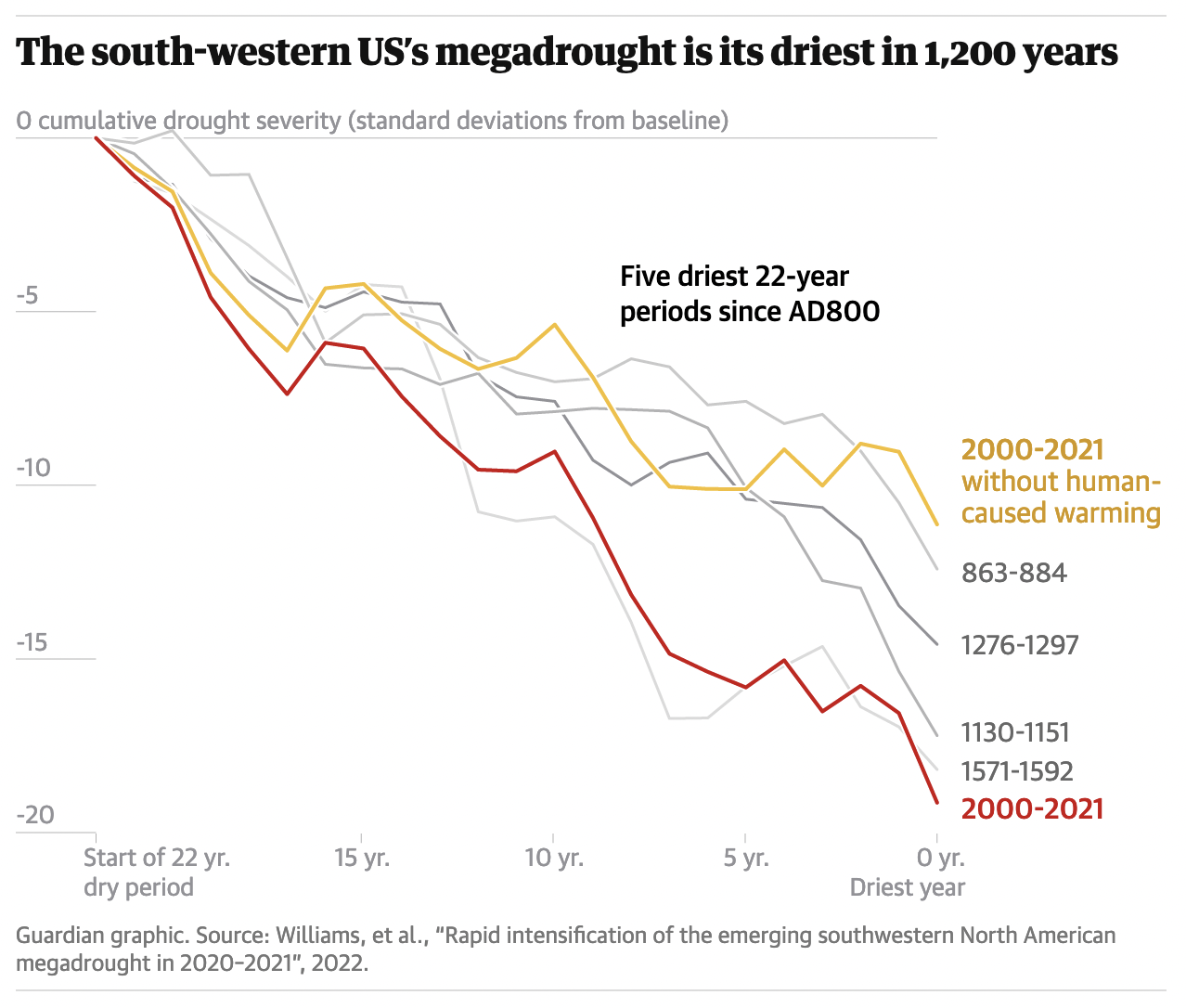
The consequences of a sweltering Earth are hitting home in the US south-west and mountain west – comprising states from California to Colorado. Over the past two decades, extreme heat and dwindling moisture levels have converged to create a “megadrought” deemed the driest period in 1,200 years.
The west is now in uncharted territory, as once singular conditions become the norm. Its mightiest reservoirs – Lake Mead and Lake Powell – are at record low levels and steadily shriveling. Prolonged, triple-digit heatwaves are making cities like Phoenix, Arizona, and Las Vegas, Nevada, almost unlivable during summers. And wildfires now spark year-round as parched forests and grasslands are more primed than ever to burn.
“We were given an excellent warning by climate scientists,” says Bill McKibben, the journalist turned climate activist. “And, yet, instead of mustering the will to do something about it, our political and economic systems rallied to do nothing.”
While drought is a natural part of the south-west’s climate, looking at the relationship between tree rings and soil moisture found that the current period of aridity, which began in the year 2000, is unprecedented since AD800. The 2022 study, published in the journal Nature Climate Change, attributed 42% of the last two decades’ hot and dry conditions to global heating.

Tim Kohler, an archaeologist and professor at Washington State University, says the current megadrought is different from prehistoric dry periods. “This one seems to be more severe than any of the previous droughts and just as long,” he says. “But the really bad news is all the previous megadroughts took place without the influence of increasing greenhouse gases. Now we are playing a new ballgame and scientists don’t know what to expect.”