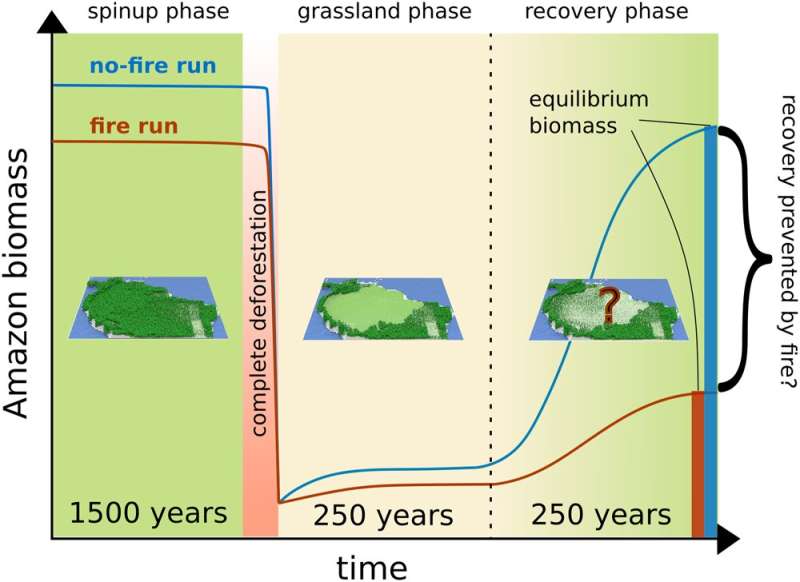
Global warming and drastic deforestation could dry out the Amazon rainforest faster and enforce the risk of keeping it downright fire-trapped. A new study published in Communications Earth & Environment shows that fire can be a decisive factor for a potential tipping of the Amazon rainforest, as it is capable of locking large parts of the Amazon in a treeless state. While naturally not occurring in rainforests, fire can play an increasing role once the forest is damaged, thinned or completely lost, up to a status where fire is the dominating driver of the ecosystem.
“It turns out, fire is the important factor for locking the Amazon in a grassland state, preventing 56%–86% of the Amazon from regrowing, depending on the strength of climate change,” lead author Markus Dr.üke from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) explains. “We know that reversing the Amazon forest loss becomes increasingly harder the more forest is lost, and our study shows that fire puts another lever onto this coherence.”
Usually, the trees of the Amazon transport enormous amounts of water back to the atmosphere, which they originally received as rain. This water can form new rain locally or downwind in a process called moisture recycling basically forming “flying rivers,” not only stabilizing the Amazon as whole but also enabling it to extent into regions that would be too dry without this process.
This coherence is the main reason why the Amazon is considered a tipping element of the Earth system. Global warming and deforestation can damage these flying rivers leading to a self-reinforcing feedback of forest loss. The new study now underlines how fire dynamics help to push and lock the Amazon towards and in a savanna-like or treeless state.