The groundbreaking modeling study published by Australian and American researchers at the end of March for the first time includes a detailed assessment of the likely impact of melting ice, revealing the importance of this past failure. It predicts a 42 percent decline in deep-water formation in the Southern Ocean by 2050. This is more than twice the 19 percent they predict for an equivalent event in the North Atlantic.
And after 2050, their model predicts that things will get even worse. Deep-water formation “looks headed towards collapse this century,” the coordinator of the study, Matthew England of the University of New South Wales, told Yale Environment 360. “And once collapsed, it would most likely stay collapsed until Antarctic melting stopped. At current projections that could be centuries away.”
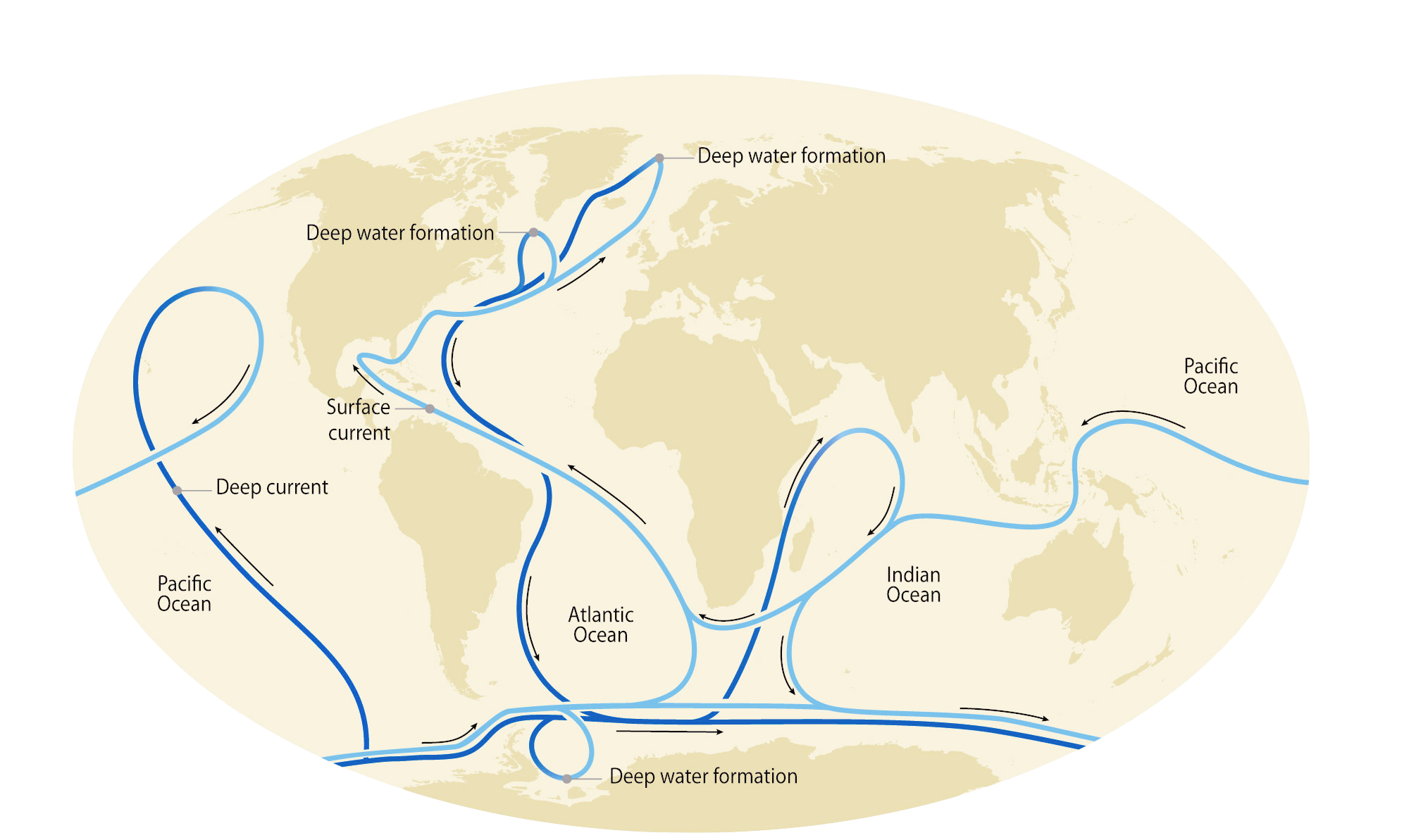
The ocean circulation system, often called the global conveyor, follows a regular path through the Earth’s oceans and stirs their waters from top to bottom. It starts with water plunging from the surface and disappearing to the depths, from where it travels the world and does not surface for centuries. By capturing heat and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and burying both deep in the ocean, it is currently moderating global warming.
The conveyor is driven by the descent of cold, salty water to the ocean floor in just two places: in the far North Atlantic near Greenland and in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica. In both regions, the mechanism is the same. In cold polar conditions, large volumes of water freeze. The salt in the water is not incorporated into the ice. It remains in the residual liquid water, which grows ever saltier. The saltier water becomes, the denser it becomes. So the residue is heavier than surrounding water and eventually sinks to the ocean floor.
About 250 trillion tons of salty water sinks in this way around Antarctica each year, subsequently spreading north along the ocean floor into the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific oceans. Similar volumes spread south from Greenland. The process is known as deep-water formation or ocean overturning, and it has continued largely unchanged for thousands of years.
But for how much longer? As the world warms, less ice is forming in the oceans at the ends of the Earth each year. At the same time, more ice on the nearby great ice sheets of Antarctica and Greenland is melting and releasing fresh water into the ocean.
As a result, surface water in the Southern Ocean and around Greenland is already becoming less salty, less dense, and so less able to sink. Since the 1990s, measurements taken from ships have shown that the water on the ocean floor, below 13,000 feet in depth, has warmed and freshened, with the trend strongest in the Southern Ocean.